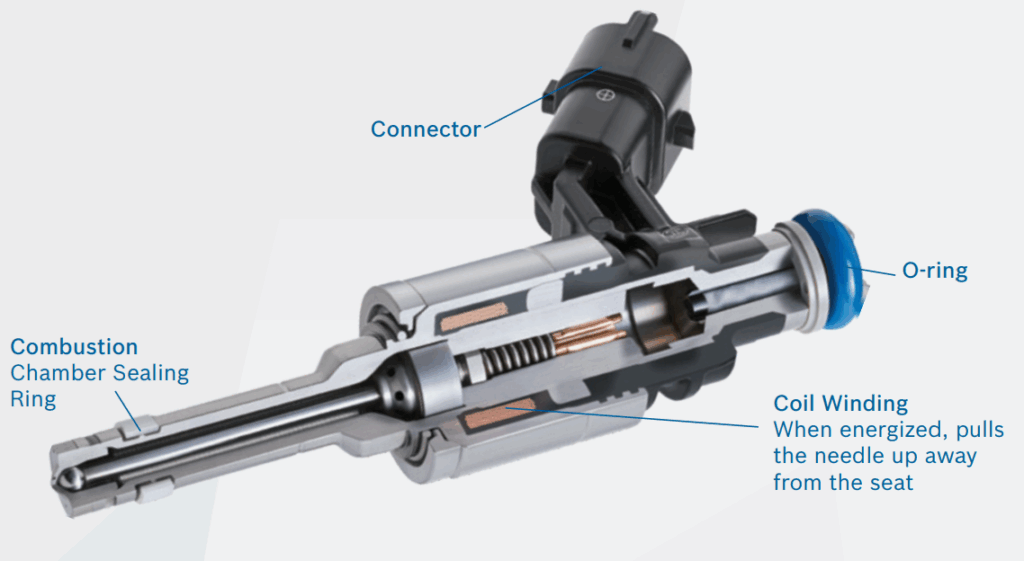
Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) injectors work by delivering fuel directly into the combustion chamber of an internal combustion engine, rather than into the intake manifold as in traditional port fuel injection systems. This direct injection system provides better fuel atomization, improved combustion efficiency, and enhanced engine performance.
How GDI Injectors Work:
- High-Pressure Fuel Delivery:
- GDI systems operate at much higher pressures (typically 500-3,000 psi) compared to port injection (30-60 psi).
- A high-pressure fuel pump, usually driven by the engine’s camshaft, pressurizes the fuel before it reaches the injector.
- Precise Fuel Injection Timing:
- GDI injectors are electronically controlled and timed to inject fuel directly into the combustion chamber at the optimal moment in the engine cycle, typically during the compression or intake stroke.
- Injector Design:
- GDI injectors have fine nozzles with multiple holes to create a fine mist, ensuring better atomization and mixing with air inside the cylinder.
- Some injectors use piezoelectric or solenoid actuators to precisely control fuel delivery.
- Spray Patterns:
- The spray pattern can be designed to target specific areas of the combustion chamber, optimizing air-fuel mixing and reducing emissions.
- Multiple Injection Events:
- Some GDI systems perform multiple injections per cycle to optimize combustion under different conditions (e.g., cold start, high load, low-speed cruising).
Advantages of GDI Injectors:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: More precise control over fuel delivery leads to better fuel economy.
- Enhanced Power Output: Direct injection allows for higher compression ratios and more efficient combustion.
- Reduced Emissions: Better control of the air-fuel mixture can lower harmful emissions such as CO2 and NOx.
- Better Cold-Start Performance: GDI allows for better vaporization of fuel in cold conditions.
Common Issues with GDI Injectors:
- Carbon Buildup: Since fuel is injected directly into the cylinder, intake valves don’t get cleaned by fuel as in port injection, leading to carbon deposits over time.
- Injector Clogging: High-pressure injectors can get clogged or fail due to fuel contaminants.
- Noisy Operation: GDI systems can be noisier compared to port injection due to high-pressure operation.
GDI Injector Maintenance Tips & Troubleshooting
Since GDI injectors operate under high pressure and deliver fuel directly into the combustion chamber, they require proper maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Here’s what you need to know:
Maintenance Tips for GDI Injectors:
- Use High-Quality Fuel:
- Choose top-tier gasoline with detergent additives to minimize carbon buildup.
- Avoid low-quality fuel that may contain contaminants or deposits.
- Regular Fuel System Cleaning:
- Use GDI-specific fuel injector cleaners that are designed to clean carbon deposits from injectors and intake valves.
- Professional intake valve cleaning (via walnut blasting or chemical cleaning) may be required periodically.
- Perform Regular Oil Changes:
- GDI engines are prone to oil dilution, where unburnt fuel can mix with the oil. Regular oil changes using manufacturer-recommended oil can help prevent engine wear.
- Periodic Intake Valve Cleaning:
- Since GDI engines do not wash intake valves with fuel, carbon buildup is common. A professional cleaning service every 30,000-50,000 miles can help maintain performance.
- Check for Fuel Leaks or Pressure Issues:
- Inspect fuel lines and injectors periodically for leaks, especially if experiencing rough idling or loss of power.
- Install a Catch Can (Optional):
- An oil catch can can help reduce the amount of oil vapors entering the intake system, minimizing carbon deposits on intake valves.
Common GDI Injector Problems & Troubleshooting:
- Carbon Buildup on Intake Valves:
- Symptoms:
- Loss of power and acceleration
- Rough idling or engine misfires
- Decreased fuel efficiency
- Solution:
- Perform an intake valve cleaning service (chemical or walnut blasting).
- Symptoms:
- Injector Clogging/Fuel Delivery Issues:
- Symptoms:
- Hesitation during acceleration
- Poor fuel economy
- Check engine light (codes related to fuel system)
- Solution:
- Use fuel injector cleaning additives or have the injectors professionally cleaned.
- Symptoms:
- Fuel Pressure Regulator or Pump Failure:
- Symptoms:
- Hard starting or no start
- Inconsistent performance under load
- Solution:
- Test fuel pressure and replace the high-pressure fuel pump if necessary.
- Symptoms:
- Injector Seal Leaks:
- Symptoms:
- Strong fuel smell
- Black smoke from the exhaust
- Rough running
- Solution:
- Replace faulty injector seals and inspect for proper installation.
- Symptoms:
- Excessive Engine Knock (Pre-ignition):
- Symptoms:
- Knocking noise during acceleration
- Reduced engine performance
- Solution:
- Use higher-octane fuel and check for carbon deposits inside the combustion chamber.
- Symptoms:
Keeping up with preventive maintenance and addressing injector issues early can help extend the life of your GDI system and keep your engine running smoothly.