To calculate fuel injector flow rate, you need to consider factors like engine power, fuel efficiency, fuel pressure, and injector duty cycle. Here’s how you can determine it:
1. Basic Formula for Fuel Injector Flow Rate
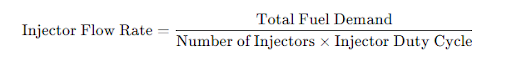
Where:
- Total Fuel Demand (lb/hr): Based on engine power and fuel consumption.
- Number of Injectors: The total number of fuel injectors.
- Injector Duty Cycle: The operating percentage (typically max 80-90% or 0.80-0.90).
2. Step-by-Step Calculation
Step 1: Calculate Total Fuel Demand
Use the formula:
Total Fuel Demand = Horsepower X BSFC
Where:
- Horsepower (HP): Engine power output.
- BSFC (Brake Specific Fuel Consumption): Fuel consumption per horsepower per hour. Typical values:
- Naturally aspirated gasoline: 0.4 – 0.5 lb/hp/hr
- Turbocharged gasoline: 0.55 – 0.65 lb/hp/hr
- Diesel: 0.35 – 0.45 lb/hp/hr
Example Calculation:
For a 400 HP engine with a BSFC of 0.50 lb/hp/hr, the total fuel demand is:
400×0.50=200 lb/hr
Step 2: Determine Injector Flow Rate
If you have 8 injectors and a duty cycle of 80% (0.80):
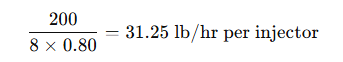
To convert to cc/min, use the conversion factor:
31.25 X 10.5 = 328 cc/min per injector
3. Adjusting for Fuel Pressure
Injectors are typically rated at 43.5 psi (3 bar). If the operating fuel pressure differs, the flow rate needs adjustment:
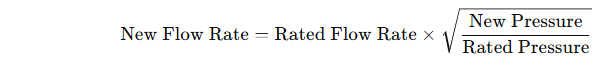
Example:
If an injector is rated at 300 cc/min at 43.5 psi, and fuel pressure increases to 58 psi, the new flow rate will be:
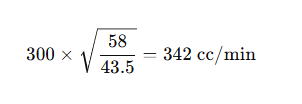
4. Common Injector Flow Rate Units Conversion
If you have flow rates in different units, use these conversions:
- 1 lb/hr ≈ 10.5 cc/min (mL/min)
- 1 cc/min ≈ 0.095 lb/hr
- 1 gallon = 3.785 liters
- 1 psi = 0.06895 bar
5. Practical Considerations
- Always leave a margin in injector sizing to avoid running them at 100% duty cycle.
- Consider future upgrades such as turbocharging or increased fuel demands.
